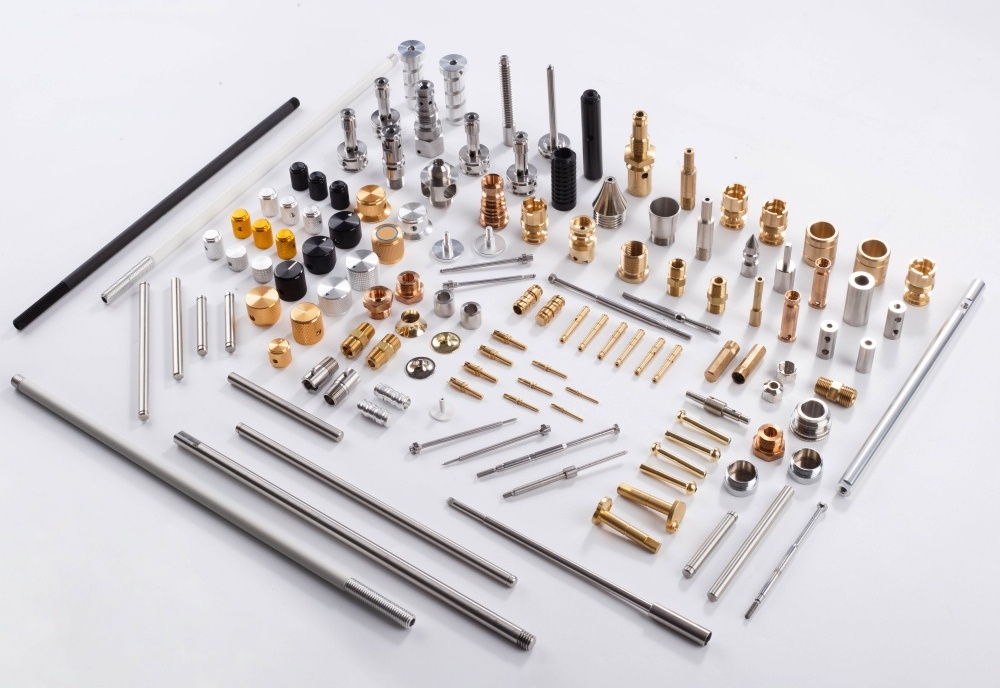
Reducing the deformation of parts during machiningis a comprehensive process that requires considering multiple aspects such as material properties, processing methods, fixture design, and cutting parameters. The following are some specific measures:
I. Optimize the blank manufacturing process
Reduce internal stress: Internal stress is generated in the blank during the manufacturing process, which may cause part deformation during subsequent processing. By methods such as natural aging, artificial aging, or vibration treatment, part of the internal stress of the blank can be eliminated, thereby reducing deformation during processing.
II. Improve cutting technology
Improving cutting technology is also crucial. High - speed cutting technology reduces cutting force and cutting heat by increasing the machine tool rotation speed and feed rate while reducing the depth of cut, thus reducing part deformation. Reasonable selection of cutting tools is also key. The material and geometric parameters of the cutting tool have a significant impact on cutting force and cutting heat. Selecting a cutting tool with a large rake angle, appropriate clearance angle, and large helix angle can reduce cutting deformation and cutting force. In addition, reducing the number of milling cutter teeth and increasing the chip - holding space also helps to reduce cutting deformation.
III. Reasonably select clamping methods and clamping forces
Fixture design: The design and selection of fixtures have a great impact on part processing deformation. A reasonable fixture design can ensure the stability of the part during processing and reduce the impact of clamping force on part deformation. For thin - walled parts with poor rigidity, methods such as axial - end - face pressing or fixtures like vacuum chucks can be used to obtain a uniformly distributed clamping force.
Clamping force control: Under the premise of ensuring that the workpiece does not loosen, the clamping force should be as small as possible. Excessive clamping force will cause part deformation. In addition, the action point of the clamping force should be on the support surface as much as possible and act in the direction of good workpiece rigidity.
IV. Reasonably arrange the processing sequence and cutting parameters
Processing sequence: A reasonable processing sequence can reduce the internal stress of the part and lower the risk of deformation. For example, rough machining can be carried out first, followed by finish machining to reduce the impact of cutting force and cutting heat on the part. For parts with a large machining allowance, symmetric machining is advisable to avoid deformation caused by heat concentration.
Cutting parameters: During the cutting process, cutting force and cutting heat can be reduced by changing cutting parameters. In numerical control machining, this goal can be achieved by reducing the depth of cut, increasing the feed rate, and increasing the machine tool rotation speed.
V. Real - time monitoring and adjustment
Processing process monitoring: Conduct real - time monitoring during the processing to detect and correct deformation in a timely manner. By monitoring parameters such as cutting force and cutting temperature, it can be determined whether the part is deformed, and corresponding adjustment measures can be taken.
VI. Other measures
Improve workpiece clamping methods: For parts with poor rigidity such as thin - walled workpieces, methods such as filling can be used to increase the process rigidity and reduce deformation during clamping and cutting.
Surface treatment: Through surface treatment processes such as anodizing, the surface characteristics of the part can be further improved or changed, enhancing the part's rigidity and anti - deformation ability.